HYSTERESIS CURVE:
The ferromagnetic materials show a certain relation between intensity of magnetization and strength of magnetic field. This property is called hysteresis.
FEATURES:
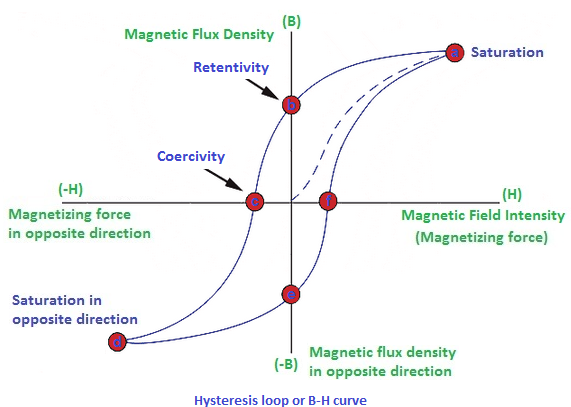
- When a substance is slowly magnetized the intensity of magnetization B increases with magnetic field intensity H. OA path is shown. At point ‘A’, magnetization becomes constant. This point is known as magnetic saturation.
- Now when H decreases, magnetization also decreases by following path AB. At ‘B’ there is some value of magnetization at zero magnetizing field H. The value of magnetization for which magnetic field intensity is zero, is called retentivity or residual magnetism.
- Further when H reversed the curved the curve BCD is obtained. As H increases in reverse direction the magnetization decreases to zero, at point C. The value OC is known as coercive force or coercivity. So coercivity defined as the magnetizing field required to destroy residual magnetism. Further increase in H a saturation point D is obtained. If now the field increases, DEFA curve is obtained.
It can be observed that throughout the cycle ABCDEFA, the magnetization lags behind magnetizing field H. Thus lagging of magnetization behind magnetic field is known as hysteresis and the path ABCDEFA is known as hysteresis loop.
PRESENTED BY:-Iswar kumar pradhan(lect. in physics)